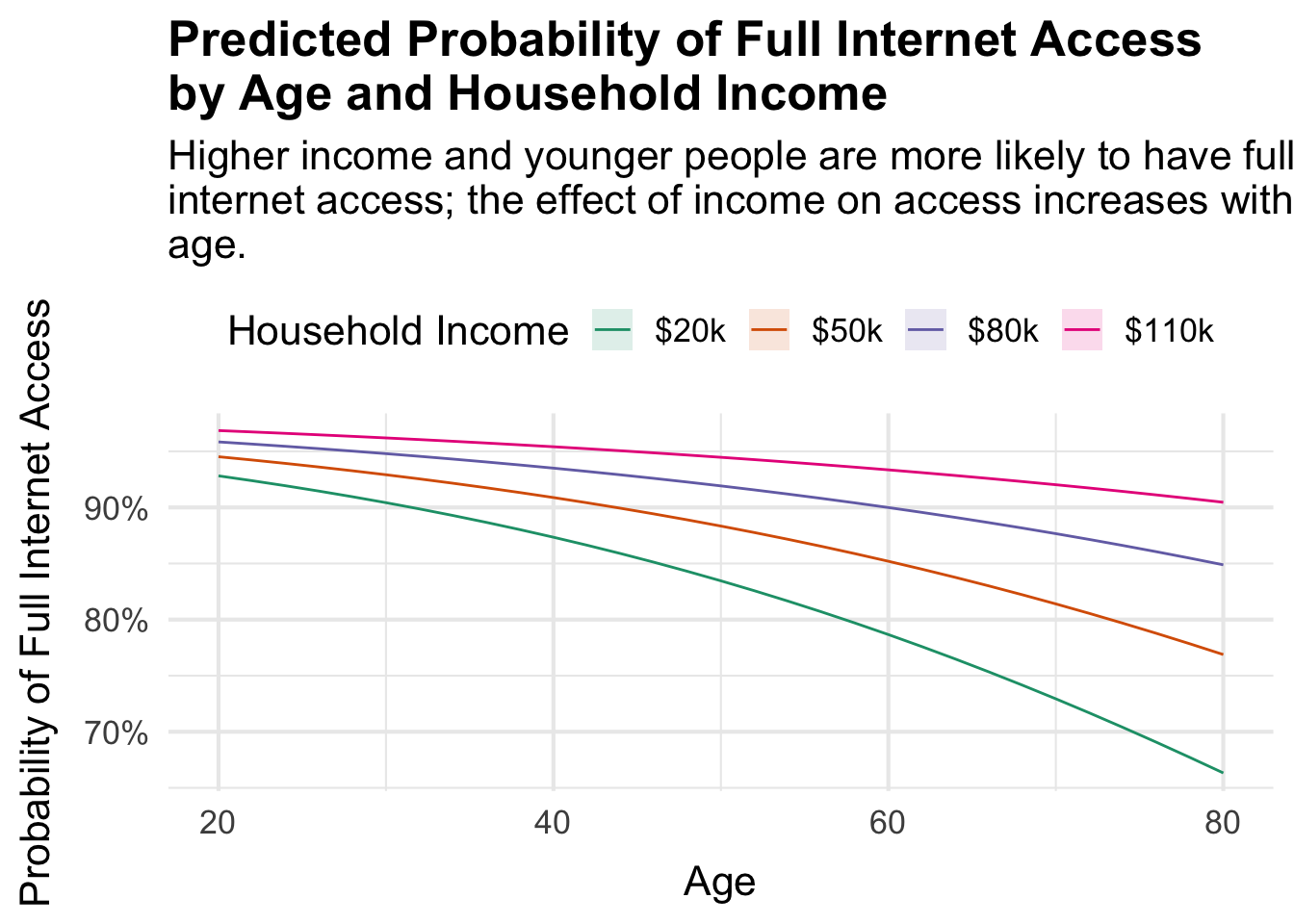
Over the past several decades access to the internet has become much more universal across America; however, some families still do not have steady access to the internet. Using data from the 2021 5-year American Community Survey, I sought to determine the impact of household income and age on Americans’ access to the internet. I modeled internet access (a binary variable) using logistic regression. While increases in income were associated with increased log-odds of internet access, increases in age were associated with decreased log-odds of internet access. Holding income constant, for every one year increase in age, the odds of full internet access decreases by roughly 3%, and the effect of income on internet access increases with age.